Homework 7
Sensitivity Analysis and DOE
1. Sensitivity Analysis
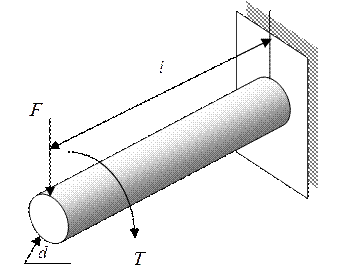
The limit-state function of a shaft in a speed reducer is defined by the difference between the strength and the maximum equivalent stress. It is given by
![]()
where
![]() mm, the diameter
of the shaft
mm, the diameter
of the shaft
![]() mm, the length of
the shaft
mm, the length of
the shaft
![]() the external force
the external force
![]() the external
torque
the external
torque
![]() the yield strength
the yield strength
The distributions of the independent random variables are given below.
Table 1 Distributions
|
Variables |
Mean |
Std |
Distribution |
|
External force |
2000 N |
220 N |
Normal |
|
Torque |
450 N·m |
50 N·m |
Normal |
|
Strength |
250 MPa |
30 MPa |
Normal |
Use the MPP result from
2.
DOE
Piston slap is unwanted vehicle engine noise caused by piston secondary motion. For understanding the problem, DOE is performed. Three parameters (clearance, length, and offset) are considered as design variables. The DOE matrix and the experimental results from a 2-level full factorial design for the noise are obtained as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 DOE Matrix and Experimental Results
|
Experiments |
Clearance: X1 |
Length: X2 |
Offset: X3 |
Noise: Y (dB) |
|
1 |
15 |
21 |
0.5 |
55.17 |
|
2 |
85 |
21 |
0.5 |
62.37 |
|
3 |
15 |
24 |
0.5 |
52.05 |
|
4 |
85 |
24 |
0.5 |
65.33 |
|
5 |
15 |
21 |
1.3 |
57.11 |
|
6 |
85 |
21 |
1.3 |
55.27 |
|
7 |
15 |
24 |
1.3 |
53.98 |
|
8 |
85 |
24 |
1.3 |
58.22 |
1) Create a DOE model with the following form:
![]()
2) A design is given in Table 2. A failure is defined as the event when the noise exceeds 63 dB. Use Monte Carlo Simulation to calculate the probability of failure and reliability of the design.
Table 2 Distribution of Random Variables
|
Random variables |
Distribution |
|
X1 |
Normal, mean = 80, std =0.5 |
|
X2 |
Normal, mean = 23, std =1 |
|
X3 |
Uniform, a = 0.9, b = 1 |
Solution: ![]() (Your solution may
be slightly different.)
(Your solution may
be slightly different.)